It’s no secret that asteroids pass close to Earth from time to time.
There are currently around 1,000 asteroids that cross Earth’s orbit on a regular basis.
Range of Sizes

Asteroids range in size from 329 miles across to just 33 feet.
329 miles is the distance from New York to Augusta, while 33 feet is the length of a roll of wallpaper or two giraffes stacked on top of one another.
How Much Damage Can They Do?

Most rocks that hit earth’s atmosphere burn up on impact, which is how we get shooting stars and meteor showers.
For a rock to hit the ground, it would have to be huge to begin with because so much would be lost in the atmosphere. Even a meteor the size of a tennis court failed to make it to the ground in 2013. Although it still caused damage because it exploded in the air and released more energy than a nuclear bomb.
Depends on the Location

How much damage an asteroid could do would depend on the location where it hit.
If it were in an isolated place, the damage would be less significant. But if one were to explode over a city such as London or New York, the damage could be widespread even if it didn’t hit the ground. There would be heat damage and blast damage to buildings and people.
Asteroid 2024 MT1 8th July

The asteroid which is passing Earth on the 8th July 2024 is 260 feet long.
That’s as big as the Statue of Liberty. It was detected and tracked by NASA’s Near-Earth Object Observations Program which keeps an eye on anything that might be a threat.
Unlikely to do Damage

2024 MT1 is unlikely to hit Earth or cause any damage.
It will pass us around 933,000 miles away which is about four times the distance from us to the moon. It is travelling at a staggering 40,600 miles per hour – hence the need for it to be monitored.
NASA’s Observations Program

NASA’s Near-Earth Object Observations Program observes and tracks objects that approach the Earth from space.
It uses telescopes and radar to detect objects from the ground. Although the tracking of 2024 MT1 has now passed over to NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena. This provides data such as the asteroid’s position, speed and distance from Earth.
Ground-Based Strategies

NASA has a Planetary Defense Coordination Office which works on strategies to combat any potential damage from asteroids hitting Earth.
Although no impact or damage is expected from 2024 MT1, there are still strategies in place just in case. One of the possible actions could be to try and deflect the asteroid by crashing a space craft into it.
An End to Civilisation?

We know that the dinosaurs were wiped out by an asteroid. Could that happen to us?
Thankfully not at any time in the next century thanks to early warning systems that can track the orbits of larger asteroids decades ahead of time. Smaller asteroids that can cause catastrophic regional damage are harder to track and these are the ones to watch out for.
Exciting for Some

The close approach of 2024 MT1 isn’t a scary prospect for everyone.
Many astronomers and space enthusiasts are excited at the chance to catch a glimpse of the asteroid and it is hoped that much can be learnt from its composition and structure.
Asteroid Detection: Earth’s First Line Defense

Scientists use advanced telescopes to scan the skies for potentially hazardous asteroids. NASA’s Center for Near Earth Object Studies (CNEOS) tracks over 28,000 near-Earth asteroids.
Astronomers discover approximately 3,000 new near-Earth asteroids each year. The Catalina Sky Survey in Arizona has discovered about 47% of all known near-Earth asteroids.
Impact Probability: Calculating Cosmic Collision Chances
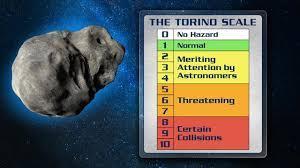
Astronomers use complex mathematical models to calculate an asteroid’s trajectory and impact probability. The Torino Scale, ranging from 0 to 10, assesses the risk of asteroid impacts.
As of 2023, no known asteroid poses a significant threat to Earth in the next 100 years. Did you know? The 1908 Tunguska event, likely caused by an asteroid, flattened 2,000 square kilometers of Siberian forest.
Planetary Defense: Strategies to Deflect Asteroids

Scientists develop methods to deflect asteroids that pose a threat to Earth. NASA’s DART mission successfully altered an asteroid’s orbit in 2022, proving the kinetic impact technique.
Other proposed methods include gravity tractors and nuclear devices. The United Nations established International Asteroid Day on June 30th to raise awareness about asteroid impact hazards.
Asteroid Composition: Unraveling Space Rock Mysteries

Asteroids can be classified as C-type (carbonaceous), S-type (silicaceous), or M-type (metallic). The largest known asteroid, Ceres, measures 940 kilometers in diameter.
Scientists study asteroid samples to understand the early solar system’s formation. Did you know? The asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter contains millions of asteroids, but they are spread over a vast area.
Historical Impacts: Earth’s Cosmic Collision Record
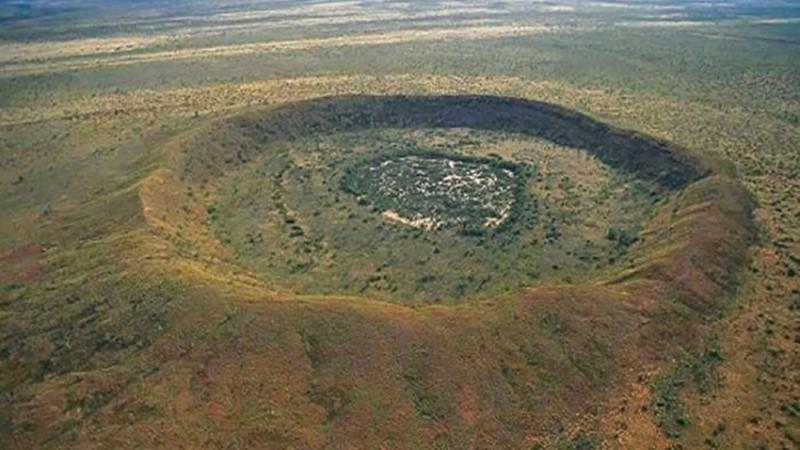

The Chicxulub impact 66 million years ago likely caused the extinction of non-avian dinosaurs. Scientists have identified over 190 confirmed impact craters on Earth.
The Vredefort crater in South Africa, with a diameter of 300 kilometers, is the largest known impact structure on Earth. Did you know? Microscopic remnants of ancient impacts, called spherules, have been found in sedimentary rocks worldwide?

